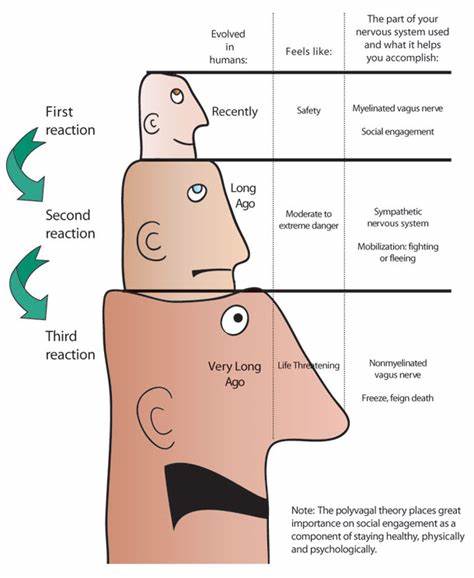
Introduction:
The human body is a complex and intricate system, and the Vagus Nerve is an important part of it. The Vagus Nerve is one of the longest nerves in the body, and it has many functions that are essential for maintaining the proper functioning of our body. In this article, we will explore the anatomy and functions of the Vagus Nerve, as well as the disorders that are associated with it. Additionally, we will discuss techniques to stimulate the Vagus Nerve, which can have positive effects on our physical and mental health.
Anatomy of the Vagus Nerve
The Vagus Nerve is the tenth cranial nerve, and it is the longest nerve in the body. It originates from the medulla oblongata, which is a part of the brainstem, and extends down to the abdomen. The Vagus Nerve is composed of both sensory and motor fibers, and it is responsible for the control of many important bodily functions, including heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
The Vagus Nerve has two main branches: the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the auricular branch. The recurrent laryngeal nerve innervates the larynx, while the auricular branch innervates the outer ear. Additionally, the Vagus Nerve has several other branches that innervate different organs and tissues throughout the body.
Functions of the Vagus Nerve
The Vagus Nerve is an essential part of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” response in the body. It regulates many important bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiration.
One of the primary functions of the Vagus Nerve is to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. It does this by sending signals to the heart to slow down or speed up, depending on the body’s needs. This helps to maintain a steady heart rate and prevent fluctuations in blood pressure.
The Vagus Nerve also plays an important role in digestion and gut-brain communication. It helps to regulate the production of stomach acid, digestive enzymes, and bile, which are all important for the proper breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food. Additionally, the Vagus Nerve helps to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
In addition to its role in the digestive system, the Vagus Nerve also plays a crucial role in the respiratory system. It helps to regulate breathing by sending signals to the diaphragm and other muscles involved in breathing. It also helps to regulate the diameter of the airways, which can help to prevent respiratory distress.
Finally, the Vagus Nerve plays an important role in the immune system. It helps to regulate inflammation, which is a key component of the immune response. Inflammation is important for fighting off infections and healing injuries, but excessive inflammation can lead to chronic diseases such as arthritis, asthma, and autoimmune disorders. The Vagus Nerve helps to regulate inflammation by releasing anti-inflammatory neurotransmitters.
Disorders Associated with the Vagus Nerve
The Vagus Nerve is involved in many bodily functions, and disorders that affect the nerve can have a wide range of effects on the body. One such disorder is epilepsy, which is a neurological disorder characterized by seizures. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Therapy (VNS) is a treatment option for patients with epilepsy who have not responded to other forms of treatment. VNS involves the implantation of a device that sends electrical signals to the Vagus Nerve, which can help to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Another disorder associated with the Vagus Nerve is anxiety and depression. Studies have shown that stimulating the Vagus Nerve can have a positive effect on mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. VNS has been approved by the FDA as a treatment option for patients with treatment-resistant depression.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is another disorder that is associated with the Vagus Nerve. The nerve plays a crucial role in the communication between the gut and the brain, and disturbances in this communication can contribute to the development of IBD. VNS has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of IBD, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and inflammation.
Finally, Alzheimer’s Disease is another disorder that is associated with the Vagus Nerve. Studies have shown that stimulating the nerve can help to improve cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. VNS is currently being studied as a potential treatment option for patients with Alzheimer’s Disease.
Techniques to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve
There are several techniques that can be used to stimulate the Vagus Nerve, which can have positive effects on both physical and mental health. One of which involves taking slow, deep breaths, which can help to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and stimulate the Vagus Nerve. This can help to reduce stress and anxiety, lower blood pressure, and improve digestion.
Meditation is another technique that can be used to stimulate the Vagus Nerve. Meditation involves focusing the mind on a particular object, such as the breath, and letting go of distracting thoughts. This can help to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and stimulate the Vagus Nerve, leading to a sense of relaxation and calm.
Acupuncture is another technique that can be used to stimulate the Vagus Nerve. Acupuncture involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body, which can help to regulate the flow of energy and activate the parasympathetic nervous system. This can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation.
Polarity Therapy is also another technique where the practitioner uses their hands to stimulate the vagus nerve with diaphragm opening, ear release, as well as creating balance in the nervous system.
Electrical stimulation is a more invasive technique that can be used to stimulate the Vagus Nerve. VNS involves the implantation of a device that sends electrical signals to the Vagus Nerve, which can help to regulate various bodily functions, such as heart rate, respiration, and inflammation. VNS is currently used as a treatment option for patients with epilepsy, depression, and other disorders.
Finally, singing or chanting is another technique that can be used to stimulate the Vagus Nerve. Singing or chanting involves the rhythmic vibration of the vocal cords, which can help to stimulate the nerve and activate the parasympathetic nervous system. This can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
Dr. Stephen Porges has created the Safe & Sound Therapy which is a series of sound frequencies to be listened to over a 5 hour period in 5 sessions. In our work, the integration of Safe & Sound combined with Meditation, Polarity Therapy, and Energy Work have proven to show quick results for clients experiencing difficulty in self-regulating.
[bookly-form location_id=”3″ category_id=”18″ service_id=”85″]Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Learn more about the founder and vagus nerve therapy through sound right here.